Introduction
In the rapidly evolving manufacturing sector, the need for operational efficiency and reliability has never been more pressing. Manufacturers are increasingly turning to Condition Monitoring (CM) and Predictive Maintenance (PdM) as strategic approaches to enhance equipment reliability, minimize downtime, and optimize overall operational performance. These methodologies utilize advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning to monitor equipment health in real-time, predict potential failures, and schedule maintenance activities proactively. This article delves into the innovations driving these strategies, explores various use cases, highlights successful solutions, outlines a structured approach for implementation, and discusses the challenges and measurable outcomes associated with adopting CM and PdM.
Innovations and Methods in Condition Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
The landscape of maintenance strategies has undergone a significant transformation from reactive to predictive models. Key innovations include:
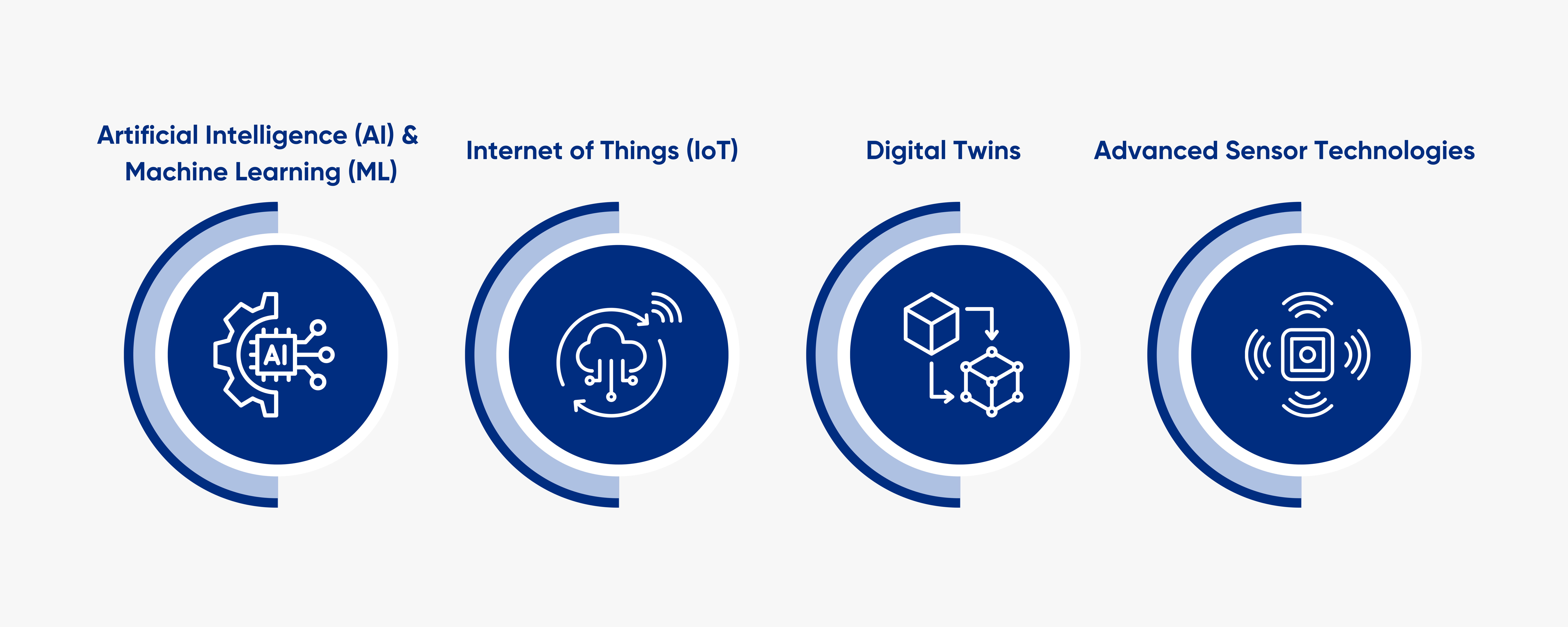
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): These technologies analyze vast datasets generated by sensors to identify patterns that indicate potential equipment failures. For instance, machine learning algorithms can predict failure probabilities based on historical performance data, enabling manufacturers to intervene before issues escalate.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices facilitate continuous data collection from machinery, providing a comprehensive view of operational health. These devices can monitor various parameters such as temperature, vibration, and acoustic emissions, which are critical for assessing equipment performance.
- Digital Twins : By creating a virtual replica of physical assets, digital twins allow manufacturers to simulate different operational scenarios. This technology aids in predicting how changes in processes or environments might affect asset performance over time.
- Advanced Sensor Technologies: Modern sensors can capture a wide range of data points including vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and oil condition monitoring. These sensors provide granular insights into equipment health, enabling more precise maintenance interventions.
Use Cases and Solutions
Numerous industries have successfully integrated CM and PdM into their operations, yielding significant benefits:
- A leading industrial manufacturer implemented AI-driven predictive maintenance across its manufacturing facilities, resulting in a 20% increase in equipment uptime and a 10% reduction in maintenance costs. By leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze sensor data from machinery, the company was able to predict failures with high accuracy.
- A leading industrial technology company adopted predictive maintenance for its wind turbine operations. By utilizing AI-powered monitoring systems that analyze real-time data from turbines, the company improved reliability and reduced maintenance costs significantly. This proactive approach allowed for timely scheduling of maintenance activities based on actual performance data rather than fixed intervals.
- A leading construction equipment manufacturer utilizes condition monitoring systems with IoT sensors to provide real-time insights into equipment health on construction sites. This system has enabled the company to reduce unplanned downtime by up to 30%, enhancing productivity across its operations.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
The advantages of implementing predictive maintenance strategies are manifold:
- Reduced Downtime: By predicting equipment failures before they occur, manufacturers can schedule maintenance during non-productive hours, significantly reducing unplanned downtime.
- Cost Savings: Predictive maintenance minimizes emergency repairs and unnecessary routine maintenance costs by ensuring that interventions are only made when necessary. A study indicated that businesses could achieve up to 15% cost reductions through effective PdM strategies.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Continuous monitoring allows for early detection of potential issues, preventing severe damage that could lead to costly replacements or extensive repairs.
- Enhanced Safety: Proactively identifying potential hazards reduces the risk of accidents related to equipment failures, thereby improving workplace safety standards.
Approach for Successful Implementation
To effectively implement CM and PdM strategies, organizations should follow a structured approach:

- Assessment of Current Practices: Conduct a thorough evaluation of existing maintenance practices to identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Technology Investment: Invest in appropriate IoT sensors, AI analytics tools, and software platforms tailored to specific operational needs. This may include condition-indicating sensors for vibration analysis or thermal imaging cameras for heat detection.
- Data Integration: Develop a robust data infrastructure that integrates real-time sensor data with historical maintenance records. This holistic view enables better predictive analytics.
- Training and Change Management: Provide comprehensive training for staff on new technologies and foster a culture that embraces data-driven decision-making.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review system performance metrics to refine predictive models and improve accuracy over time. Implement feedback loops that allow for iterative enhancements based on real-world outcomes.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite the clear benefits, several challenges can impede the successful implementation of CM and PdM systems:
- Data Quality Issues: Effective predictive maintenance relies on high-quality data from sensors. Inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to incorrect predictions and poor decision-making.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating new technologies with existing legacy systems can be complex and resource intensive. Organizations may face compatibility issues that require careful planning.
- Resistance to Change: Employees accustomed to traditional maintenance practices may resist adopting new technologies or methodologies. Overcoming this cultural barrier is essential for successful implementation.
- High Initial Costs: The upfront investment required for sensors, software solutions, and training can be substantial. Organizations must carefully evaluate the long-term ROI against initial expenditures.
Outcomes Achievable Through Predictive Maintenance
The successful implementation of CM and PdM strategies can lead to transformative outcomes:
- Increased operational efficiency through optimized resource allocation.
- Enhanced asset reliability leading to improved production quality.
- Significant reductions in unplanned downtime translating into higher profitability.
- Strengthened competitive advantage in an increasingly dynamic manufacturing environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as manufacturers continue to embrace condition monitoring and predictive maintenance driven by advanced technologies like AI and IoT, they position themselves not only to minimize downtime but also to enhance overall operational efficiency. The proactive nature of these approaches ensures that businesses can respond swiftly to potential issues before they escalate into costly problems, ultimately driving long-term success in an increasingly competitive market.