Approach to Actionable Insights
Data Transformation Process
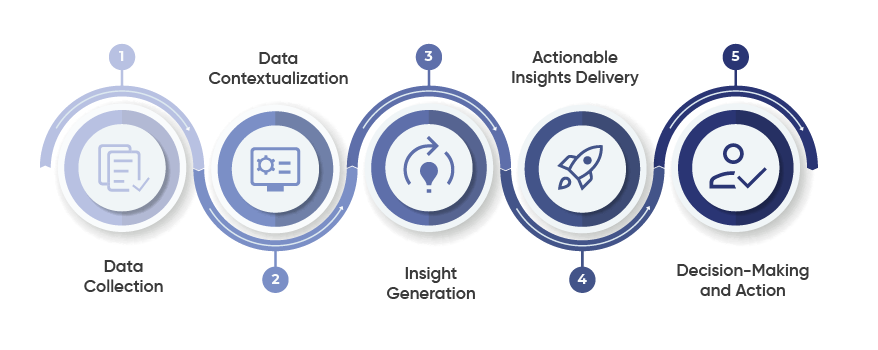
1. Data Collection
The first step involves gathering data from various sources, including machinery, production lines, and quality control systems. For example, a manufacturing facility might deploy IoT sensors to capture real-time data on machine performance and production output.
2. Data Contextualization
Raw data must be contextualized to become meaningful information. This involves organizing the data in a way that highlights relevant patterns and trends. For instance, using manufacturing dashboards can visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production rates and defect counts, making it easier for managers to identify anomalies quickly.
3. Insight Generation
Once the data is organized, analytics tools can analyze it to generate insights. For example, if a factory notices an increase in defective products from a specific line, the system can trigger alerts to notify supervisors immediately. These insights are often derived through historical comparisons and trend analyses, allowing stakeholders to understand the underlying causes of issues.
4. Actionable Insights Delivery
The insights generated must be delivered to the right stakeholders in a timely manner. This can be achieved through automated reporting systems that send alerts or notifications when predefined thresholds are breached. For instance, if machine temperature exceeds a safe limit, an automated alert can be sent directly to maintenance personnel for immediate action.
5. Decision-Making and Action
With actionable insights at their fingertips, stakeholders can make informed decisions about the next steps. This could involve scheduling maintenance for malfunctioning equipment or reallocating resources to address production bottlenecks. For example, a plastics factory supervisor might notice a spike in defects and decide to halt production on that line until further investigation is conducted.
Use Case
- Threshold Breach Detection: The monitoring system identifies the drop in real-time.
- Automated Alert: An alert is automatically sent to the production manager’s dashboard.
- Stakeholder Notification: The system notifies relevant team members via email or mobile app.
- Next Best Action: The production manager reviews the data and decides whether to investigate machine settings or inspect the workforce for potential issues.
Solutions for Optimizing Manufacturing Operations
Predictive Maintenance
- Case Study: In an automotive assembly plant, predictive maintenance systems monitor critical machinery like robots and conveyors. By detecting early signs of wear, maintenance teams can schedule interventions proactively, preventing costly production delays.
Workload Optimization Tools
- Case Study: A leading manufacturer implemented Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) strategies focused on proactive maintenance and continuous improvement. By optimizing machine performance through planned maintenance schedules and systematic problem-solving, they achieved high Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
Closed-Loop Quality Systems
- Case Study: A leading aerospace manufacturer uses closed-loop systems to monitor key parameters during production. Real-time adjustments are made based on data feedback, significantly reducing defect rates and ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards.
Challenges in Implementing Actionable Insights

Data Silos
Fragmented data across departments complicates the ability to derive cohesive insights.
Integration Complexity
Merging new technologies with existing systems can be resource-intensive.

Skill Gaps
There is often a shortage of skilled personnel capable of analyzing complex data sets and implementing advanced technologies.
Outcomes Achievable Through Actionable Insights

Increased Operational Efficiency
Companies utilizing data-driven decision-making report a 20-25% increase in operational efficiency.

Reduced Downtime
Predictive maintenance strategies can cut downtime by 15% or more.

Enhanced Product Quality
Closed-loop systems contribute to lower defect rates and improved customer satisfaction.

Cost Savings
Proactive maintenance reduces emergency repair costs significantly; for instance, one company reported reducing planned downtime to just 0.75% due to effective predictive strategies.