Hyper-personalization is changing the banking landscape in many regards, customer acquisition included. We’ve long progressed into the digital age, and consumers expect banks to realize their needs in this economic setting. Every consumer has different needs, and due to social algorithms and targeted ads, we expect every business to engage with us based on the current context of our lives, lifestyle, events, and financial status included.
Most banking organizations have not missed this fact. New techniques and technologies have come to light that will help financial institutions assess how they can successfully create a hyper-personalized acquisition, but it starts with genuinely understanding the behaviors and lifestyles of their current and potential consumers.
From a Consumer Point of View
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, consumers adopting digital technologies increased, showing no signs of slowing down in the imminent future. Today, customers generally expect banks to know what makes them tick, encompassing their unique needs and personal expectations. Even ten years ago, we’d barely imagined the idea of technology understanding customers personally without ever speaking to them.
However, today many financial institutions are trying to see things from a consumer P.O.V., which is essential to the survival of every business. Gone are the days when services that human beings need can conduct business however they want and still retain customers.
Some (definitely not all) financial sector institutions continue to take a business approach that doesn’t focus on personalization, resulting in low consumer engagement and conversion rates. They are forever irritating their would-be customer base with irrelevant offers and communication products that will not suit their current lifestyle.
The bottom line: customers want to feel seen and heard, even by massive corporations. They also want offers that provide a solution to the current lifestyle struggles they’re facing, whether that be a tailored retirement savings account or zero money down for first-time homebuyers.
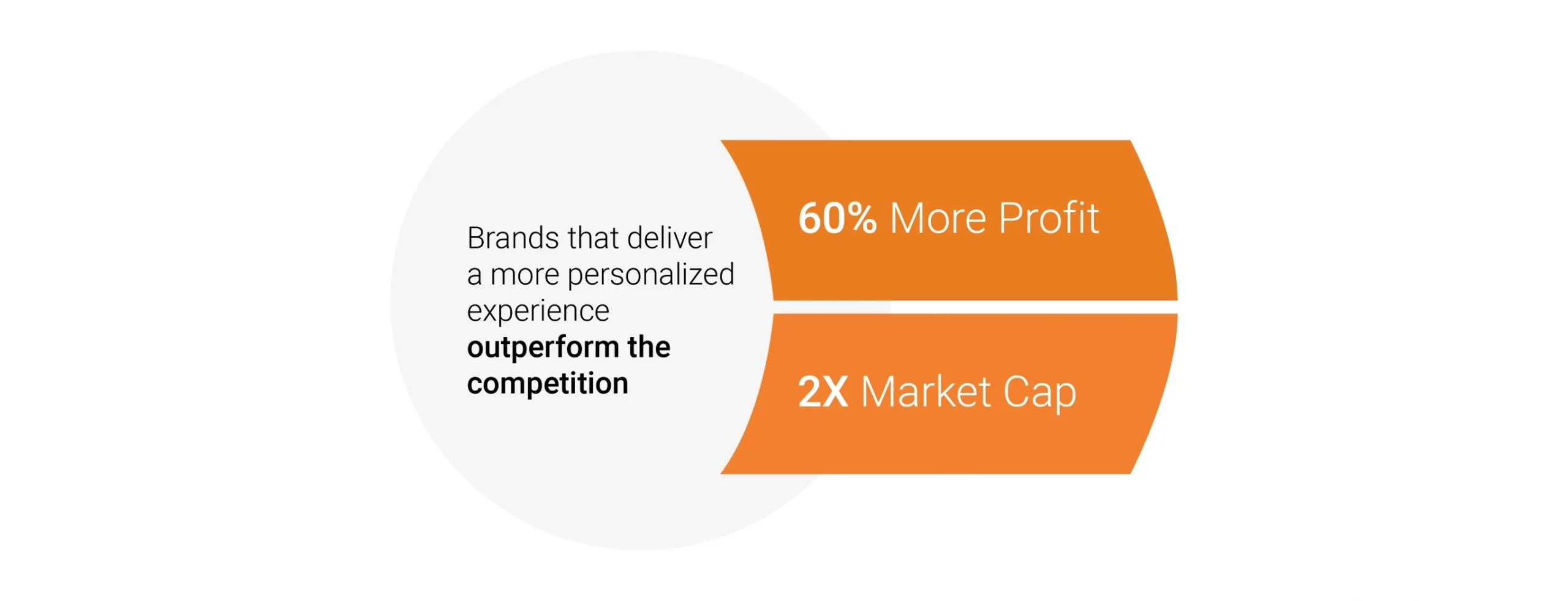
A Look at Hyper-Personalization for Banking
Hyper-personalization in banking is becoming an integral component. This concept is not subject to banks only, as everyone that offers services in the financial industry should want to consider doing the same. Banks focus more on the customer experience than they ever have in the past, offering users tailor-made services that make an actual difference in their lives.
Modern consumers are more acclimated to hyper-personalized approaches than others. Companies of all sizes grow and expand because of their ability to offer a unique selling point to millions of people. A substantial number of banks have begun to utilize hyper-personalization, but others struggle to adopt the technology that can handle analyzing the vast amounts of data.
Hyper-personalization in banking is a distinctive approach that offers personalized products to its clients. The practice bases itself on behavioral science and AI (artificial intelligence) product recommendations compiled from the data collected from customer transactions, location, and shopping habits.
Artificial intelligence utilizes customer data to come up with complete profiles that banking institutions can later use to create product offers that cater to the changing needs of their consumers. It’s important to note that the future success of the financial sector likely depends on maintaining the balance between data protection and technology-based services.
Harnessing the Power of Technology-Based Banking
Modern banking is long past, entering a new era, and there’s no going back. Today, it’s common to combine AI and behavioral analytics to provide customers with the services they want through personalized recommendations. Unlocking the power of customer data means aggregating that data on cloud services across varying department sections.
Utilizing genuine customer profiles that reflect everything from financial capacity to spending habits makes it possible to get super personalized. Digital banking is now imperative, and to keep up, banks have to invest more time and resources into data management to maximize their digital modernization efforts.
Digital customer profiles, for example, can help banking systems determine which type of credit card offers will work best for specific individuals. These profiles can often alert banks to the right time to offer personal or business loans.
In short, hyper-personalization in the banking sector makes it very possible to serve thousands of individual clients while providing tailored services. Many industries are taking advantage of hyper-personalization, but it’s essential to examine how this type of technology can give power to the financial sector. Banks have a massive varying consumer base of all demographics, which makes harnessing the power of hyper-personalization imperative.
Implementing Hyper-Personalization
Customer adoption requires advanced digital technology. There is no way around digital transformation, and banks have to begin to see things from a customer perspective. Without question, hyper-personalization gives a competitive advantage to banking brands that want to reinforce their visibility while offering services that make sense.
For banks that want to drive growth through hyper-personalized acquisition strategies, the first step is to recognize the roadblocks in your current technology and set an increase in the IT budget. However, it takes time to understand how you can establish a level of communication with customers to create fully customized offers.
Here are a few examples.
HSBC
HSBC bank began using AI to predict the behavior of their customers through the redemption of earned spending points and then to offer them valuable rewards. Not surprisingly, HSBC noticed that their clients loved the personalization behind the new reward system and opened their company-sent emails more often. This rewards system is a fantastic example of how consumers increase their engagement when they feel heard by a larger institution.
Capital One
Another fantastic example that concerns hyper-personalization is Capital One and its method of sending clients notifications and assisting with simple tasks in managing personal finances. As you may have noticed, Capital One partnered with many retailers and utilized geolocation to prompt customers with purchase offers when they’re close to a particular retail partner. This approach is nothing short of genius.
Coming Up with a Plan
It should be clear to everyone why personalization is so effective. Pairing consumers with offers, products, and services they need drives revenue, customer satisfaction, and retention. Regardless of how well you might understand the approach, it can still be super challenging to provide impactful experiences.
One of the biggest challenges lies in learning what your customers want or need and how you can best offer those things to them. Personalization is a quick way to help your customers resolve relatively simple problems but make their banking experience difficult. Banks can try the following techniques.

The Future of Hyper-Personalized Banking
Banks continue to invest in their IT budgets, which keep rising. There has been a surge of newly formed digital banks that aim at specific demographics or communities to provide more opportunities for their customer base, giving them access to a broad range of offered financial services.
Banks that deliver incredibly personalized services will gain an advantage now and in the future, which is why so many massive brand banking names focus on developing a new, hyper-personalized way of doing. Standing institutions will find competition in digital banks because they focus on their customer’s goals instead of pushing irrelevant products.
To remain applicable, banking institutions have to really embrace hyper-personalization and apply it to almost every aspect of their operations. When you tailor your offers to what your clients truly want, you’ll find that acquisition increases exponentially.
















Recent Comments